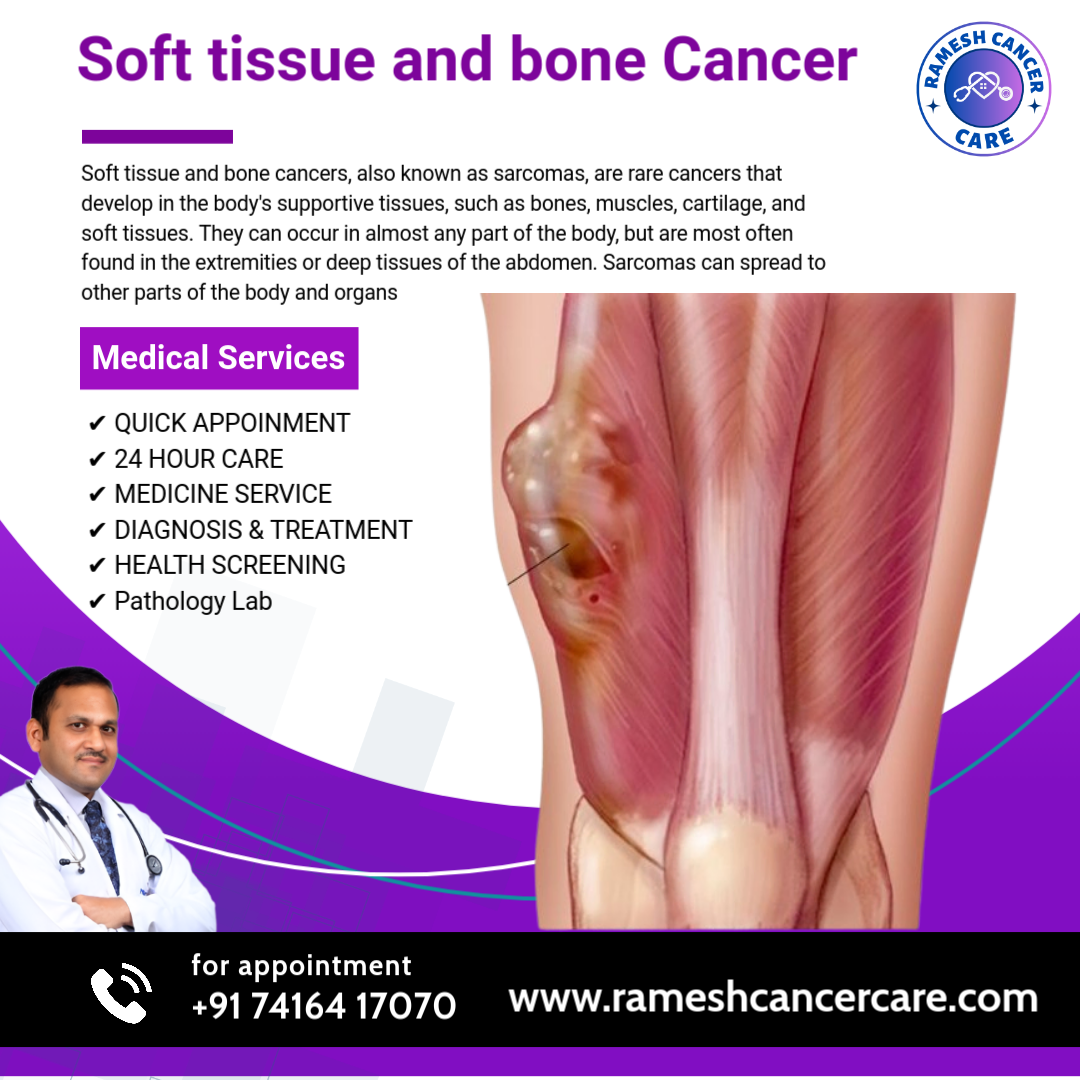
Bone and soft tissue cancer
Bone and soft tissue cancers, also known as sarcomas, are rare cancers that develop in the body's supportive tissues, such as bones, muscles, cartilag...
Dr. Ramesh Alamuri – Senior Consultant Surgical Oncologist | Laparoscopic & Robotic Cancer Surgeon
Dr. Ramesh Alamuri is a highly acclaimed Senior Consultant in Surgical Oncology, with over 13...

13+
Years Experience
5000+
Successful Surgeries
5000+
Successful Surgeries
Comprehensive Cancer Care Services

Breast CancerOverview: Breast cancer refers to abnormal growth of the cells of the breast. Though predominant in women, it is also known to occur in Men. If diagnosed at an early stage, there is a 95% chance of cure of breast cancer.What are the types of Breast cancer?Invasive ductal carcinoma: It is the most common type of breast cancer. It arises from the milk ducts and spreads to the surrounding breast tissue.Invasive lobular carcinomas: These arises from the milk-producing lobules of the breast. These tumors are multiple, and sometimes patients can have simultaneous lesions bilaterally, i.e. in both the breasts.Angiosarcoma: It is a cancer of the inner lining of blood vessels, and it can occur in any part of the body, including the breasts.Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS): It is a non-invasive cancer which affects the lining of the milk ducts in the breast. As the nomenclature ‘in situ’ suggests, this cancer remains localized. Ductal carcinoma in situ, if detected in an early stage, is highly treatable, but if left untreated or undetected, it can spread into the surrounding breast tissue.Inflammatory breast cancer: Inflammatory breast cancer is a rare type of breast cancer. It is known to develop rapidly, causing swelling, redness and tenderness in the affected breast. It develops as a result of blockage of the lymphatic vessels by cancer cells that spreads to the adjacent lymph nodes and tissues.Invasive lobular carcinoma: When cancer begins in the milk-producing glands (lobules) of the breast and has a tendency to spread to the adjacent lymph nodes and other areas of the body, it is called Invasive lobular carcinoma. This type of cancer is the second most common, following invasive ductal carcinoma.Male breast cancer: Though breast cancer is most commonly thought of as a disease that affects women, rarely, it may also occur in men. Male breast cancer is most common in older men, though it can occur at any age. Men diagnosed with male breast cancer at an early stage have a good chance of a cure.Paget’s disease of the breast: It is a rare form of breast cancer. Paget’s disease of the breast starts on the nipple and extends to the dark circle of skin (areola) around the nipple. This type of cancer occurs most often in women over the age of 50.Metastatic Breast cancer: It is a breast cancer that has spread beyond the primary site of origin in the breast and to nearby lymph nodes and other parts of the body (most often the bones, lungs, liver or brain).Non-cancerous breast conditions: Benign (non-cancerous) breast conditions are very common, and most women have them. In fact, most breast changes are benign. Some benign breast conditions have a higher risk of converting into cancer later.Non-cancerous breast conditions are not a type of Breast cancer. Mentioning below how this can be mentioned instead. Breast Cancer Signs and Symptoms: Lump in the breast/ underarmsThickening or swelling on the part of the breastDimpling of breast skinRedness or flaky skin in the nipple area or the breastPulling in of the nipple or pain in the nipple areaNipple discharge other than breast milk, including bloodNew-onset spontaneous nipple dischargeAny change in the size or the shape of the breastPain in any area of the breast

Head and neck cancers mainly start from your mouth, throat, or voice box. These cells are also called squamous cells. It is crucial to know the complexities of the diagnosis, including different types, symptoms, and diagnosis. Facing head and neck cancer can be overwhelming, both for individuals and their loved ones. This blog is a space where we will discuss various aspects of this type of cancer. Let us embark on this journey exploring the symptoms, causes, and treatment. Symptoms of Head and Neck CancerLump on the back of jaw, neck, or mouthA mouth ulcerPain or weakness in the faceNeck painDifficulty moving the jawDifficulty swallowingSpeech problemsEar pain or hearing lossNeck pain that does not go awayTrouble breathing or speakingFrequent sinus infections that won’t go awayA white or red patch in your gums, tongue, or inside the mouthPersistent sore throatFrequent headachesPlease check with your healthcare provider immediately if you notice any symptoms. They may be big signs of head and neck cancer. Causes of Head and Neck CancerHead and neck cancers mainly affect men over 50. The most common causes of this type of cancer are: TobaccoTobacco use is the most common cause of head and neck cancer. Nearly 70 to 80 % of the people suffering from this type of cancer are addicted to tobacco. Tobacco use includes smoking cigarettes, cigars, or pipes. Passive smoking can also lead to cancer. Drinking Too Much AlcoholDrinking too much alcohol can also lead to the risk of head and neck cancers. If you drink, then not more than two drinks for men and not more than one drink for women should be used per day. Human PapillomavirusHPV is also a main cause of head and neck cancer. It is a main cause, primarily among young adults. Up to 75 % of oropharyngeal cancers are associated with HPV infection. Epstein Barr VirusEBV is also a cause of head and neck cancer. It can lead to nasopharyngeal cancer. Weak Immune SystemA weak immune system makes it hard to fight cancer. HIV infection and recent major surgeries have both been associated with cancer that results from a weak immune system. Exposure to certain substancesIf you are continuously exposed to certain substances like asbestos, pesticides, wood dust, and paint, it can also increase your chances of cancer. Radiation ExposureRadiation treatment from malignant or benign tumors is also linked to salivary gland cancer. DietIncreasing too many salt-cured foods like meat and fish can increase the risk of nasopharyngeal cancer. GenesYour genes can also increase the risk of head and neck cancer. For example, people who have Fanconi Anemia inherit genes from their parents. These people are at risk of head and neck cancers. Poor Dental HygieneIf you do not take care of your teeth properly, it can increase the risk of periodontal cancer and oral cancer. Treatment of Head and Neck CancerHead and neck cancer treatment can affect teeth, gums, and mouth. Here are some things you need to do before treatment:Visiting the dentistConsult a dietitian about improving your diet and nutrition.Building up your strength by exercisingIt’s best to quit smoking because you might not respond to treatment as well as someone who doesn’t smoke.The three main treatment options are surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Your healthcare provider may also recommend new treatment options that we are going to discuss in this part of the blog: SurgeryThe main motive behind the surgery is to remove the tumor and a margin of healthy tissue surrounding it. The surgeons can also remove the lymph nodes in your neck if they suspect that cancer has spread there. Radiation TherapyIn radiation therapy, high-energy X-rays are directed toward head and neck cancers. You can receive radiation therapy as a standalone treatment or combined with other treatment options like surgery and chemotherapy. ChemotherapyIn chemotherapy, a single drug or combination of drugs is used to kill cancer cells. It is commonly used to treat advanced stages of head and neck cancers. Targeted TherapyThese drugs target specific types of cancer. They are most often used in combination with other treatments to treat advanced head and neck cancers. Cetuximab is a drug that targets a tumor protein called epidermal growth factor (EGFR) and is U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved to treat particular head and neck cancers.

Gastrointestinal (GI) cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells (cancer) in the digestive tract and other abdominal organs. There are several distinct types of GI cancers, including cancer of the esophagus, stomach, pancreas, small bowel, colon, rectum, and anus. Each cancer is different and requires special treatment. It’s important to get regular checkups and screening if you experience symptoms that concern you. Symptoms of GI Cancer: Common symptoms of cancers that affect your digestive tract, do not necessarily indicate that you have cancer. It’s essential that you get a proper diagnosis and treatment, especially if you experience the following symptoms constantly over a period of time.Abdominal painFullness in the upper abdomen after eating a small mealHeartburn or indigestionNauseaPoor appetiteVomitingWeight loss that’s unexplained Types of GI Cancer: Each part of the digestive tract may develop cancerous tissue that is unique to that part of your body, such as:Anal cancer: Signs include bleeding from the anus or rectum or a lump near the anus. This is a relatively uncommon type of cancer, treated with chemotherapy and radiation. One preventive measure is avoiding the HPV virus through safe sex practices and the HPV vaccine.Colorectal cancer: Signs include changes in bowel movements and blood in the stool. This form of cancer may start in the colon or the rectum. Regular screening for colon cancer, a colonoscopy, is widely recommended. Its purpose is early intervention and treatment.Esophageal cancer: Signs include difficulty swallowing and hoarseness. Considered a rare form of cancer, if you have Barrett’s esophagus, you will be monitored and screened for esophageal cancer, which is treated with surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.Gastric cancer: Signs include severe persistent heartburn and stomach pain. A high-fiber diet and other healthy habits can help prevent this cancer. Treatment may include surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy.Pancreatic cancer: Signs of pancreatic cancer depend on its type. Causes vary but may include smoking and obesity. Treatment is based on its type and stage.Small bowel cancer: Signs of this rare disease may include dark stool and severe diarrhea. Causes vary and Crohn’s disease may put you at risk. Treatment involves surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.

Genitourinary cancer may include cancers of the urinary system, as well as the reproductive tract. Adrenal, bladder, and kidney (also known as renal) cancers occur in the urinary system, while penile, prostate, and testicular cancers develop in the reproductive tract. Prostate, bladder, and kidney cancers are the most common types of genitourinary cancer, while testicular, penile, and adrenal cancers are the least common. People who are at higher risk of genitourinary cancer may have a family history of this type of disease. Smoking, age, race/ethnicity, chemical exposures, diet, high blood pressure, and the use of certain medicines or herbal supplements can also increase a person’s risk for certain types of genitourinary cancers.While some genitourinary cancers have obvious symptoms, others do not. For example, prostate cancer is often referred to as a "silent killer" since some patients do not report having any symptoms prior to diagnosis. However, routine physicals and screenings can help providers find and diagnose these types of cancers early. The most common types of GU cancers are prostate, bladder, and kidney cancers. Some GU cancers have obvious symptoms, but others don't. For example, prostate cancer is sometimes called a "silent killer" because some patients don't have any symptoms before diagnosis. Risk factors for GU cancers include: To diagnose GU cancers, doctors may order tests such as biopsies and imaging. Treatments for GU cancers vary depending on the type of cancer and can include surgery, chemotherapy, hormonal treatment, and immunotherapy.

Gynecological Cancers: If detected early, gynecologic cancer—including cervical, ovarian, uterine, vaginal, and vulvar— can be easily treated. However, in its early stages, patients may experience a wide range of symptoms which can be easily mistaken for other conditions. Unfortunately, currently, the only type of gynecologic cancer with a screening test is cervical cancer. For those with a family history of gynecologic cancers, genetic testing may be beneficial, depending on the type of cancer. Patients who have tested positive for human papillomavirus (HPV) are also at higher risk of developing gynecologic cancer. Gynecological cancers are cancers that affect a woman's reproductive organs, including the cervix, ovaries, uterus, vagina, and vulva. A rare sixth type is fallopian tube cancer. Each type of gynecological cancer has different signs and symptoms, risk factors, and prevention strategies. Some risk factors include:Age: The average age of a patient diagnosed with uterine cancer is 63.Some signs and symptoms of gynecological cancer include: abnormal bleeding, pelvic pain, and bloating. To prevent and detect gynecological cancers, you can: Be aware of your risk factors, Maintain a healthy lifestyle, Get routine testing and screening, and Look for potential signs and symptoms. When gynecological cancers are found early, treatment is most effective.

Thoracic cancers are malignant conditions that affect the organs and structures in the chest, including the lungs, trachea, and mediastinum. The most common types of thoracic cancers are lung cancer, esophageal cancer, and mesothelioma. Other thoracic cancers include: Lung carcinoid tumorsThymic malignanciesTracheal tumors Risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options vary by type of thoracic cancer. Some things you can do to reduce your risk of thoracic cancer include: Not smoking, Using protective equipment to avoid inhaling carcinogens, Reducing exposure to toxic substances, Maintaining a healthy diet and exercising regularly, and Getting regular physical exams. Symptoms: As thoracic cancer begins, there may be no noticeable symptoms. Abnormalities of the mediastinum are typically found on CT scans taken for other reasons. However, symptoms may include:Chest painPersistent coughNight sweatsUnexplained weight lossFever
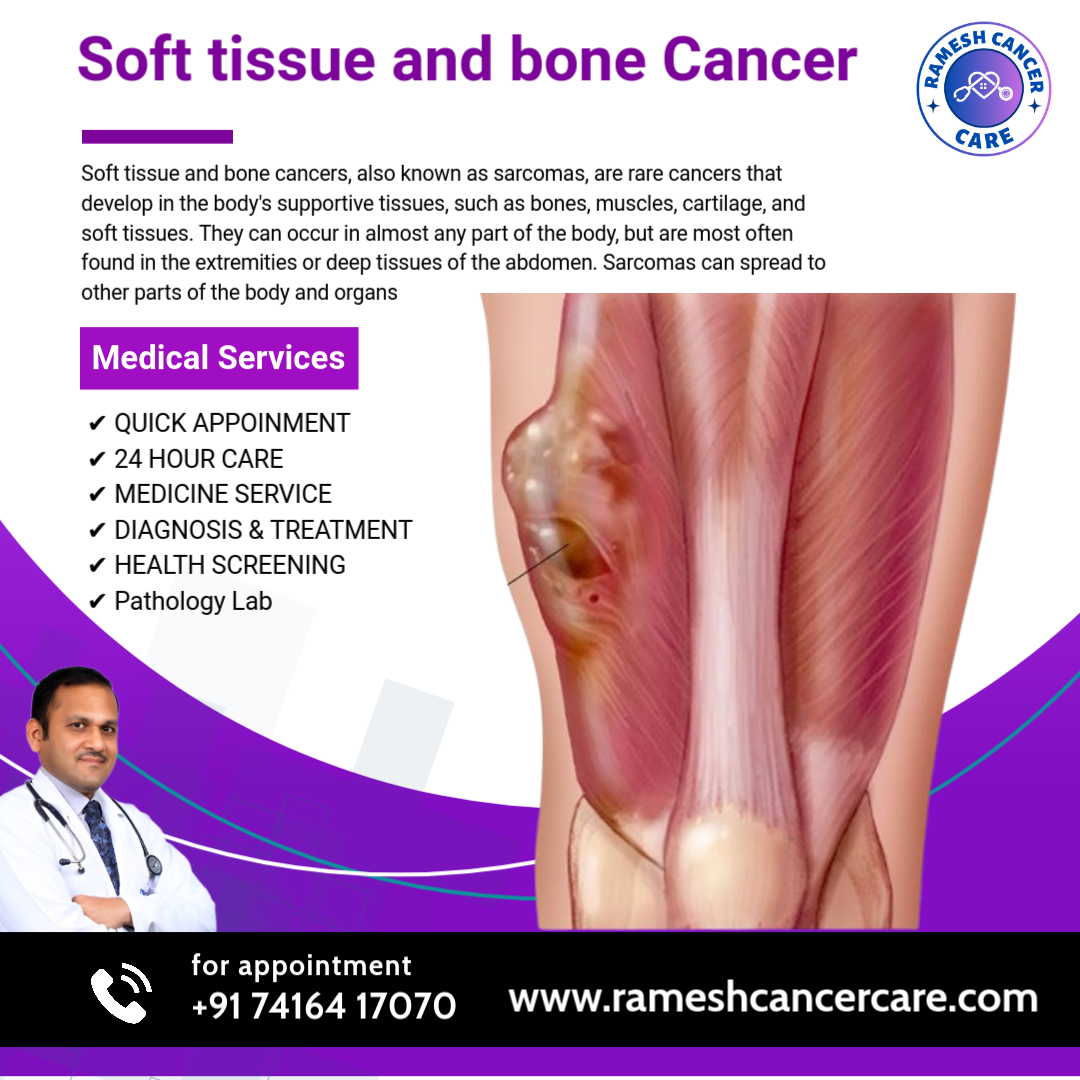
Bone and soft tissue cancers, also known as sarcomas, are rare cancers that develop in the body's supportive tissues, such as bones, muscles, cartilage, and soft tissues. They can occur in almost any part of the body, but are most often found in the extremities or deep tissues of the abdomen. Sarcomas can spread to other parts of the body and organs. Type of cancerSymptomsSoft tissue sarcomaA painless lump or swelling in the arms, legs, chest, or abdomenBone sarcomaPain and/or swelling in the arms, legs, trunk, pelvis, or backBone cancerBone pain, swelling, tenderness, weakened bone, fatigue, and weight loss Treatment options for bone and soft tissue cancers include:Surgery: Removing the tumor with a wide margin around it Chemotherapy: Often used in combination with other therapies Radiation therapy: Can include proton therapy, which uses high-intensity proton beams to destroy cancerous cells Radiofrequency ablation: A minimally invasive treatment for some bone tumors

Best doctor award from queens nri hospital
13+ Years of Experience in Oncology Treatment
best poster award in state conference of ASI
best speaker award in state conference of ASI
International Journal of Life Sciences
Successfully Treated Over 5000+ Cancer Patients
Biotechnology and Pharma Research Vol. 12, No. 4, Oct-Dec2023
What Are The Early Signs Of Cancer? | Medicover Hospitals In this video, Dr. Alamuri Ramesh, Senior consultant surgical oncologist, advance laparoscopic and robotic surgeon, Medicover Hospitals, Vizag, shares information on cancer.
In this video, Dr. Alamuri Ramesh, Senior consultant surgical oncologist, advance laparoscopic and robotic surgeon, Medicover Hospitals, Vizag, shares information on robotic surgery for cancer treatment.
Stay informed with our latest medical insights, healthcare tips, and expert advice.

Bone and soft tissue cancers, also known as sarcomas, are rare cancers that develop in the body's supportive tissues, such as bones, muscles, cartilag...

Gastrointestinal (GI) cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells (cancer) in the digestive tract and other abdominal organs. There are s...
This tool is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. If you're experiencing severe symptoms, please seek immediate medical attention.
Dr. Ramesh Alamuri is a distinguished Sr. Consultant Surgical Oncologist, Specialized in Laproscopic and Robotic Surgery, He has been Performed more than 5000 Complex Surgical Procedures. He has Experience of 13 years in the filed of surgical Oncology, He is a Member of ASI, IASO, with his extensive experience and Expertise, he has been at the forefront of innovative Cancer Treatments.